Die Homepage von Joachim Mohr
Siehe auch Wikipedia
Rechenschema für
x4+ax3+bx2+cx+d=(x2+px+q)(x2+sx+t)
Herleitung hier
Gesucht: p,q und s,t mit:
4 3 2 2 2
x + ax +bx +cx +d = (x +px+q)·(x +sx +t)
Lösung: Bestimme eine Lösung u der Gleichung 3. Grades
3 2 2 2 2
u - 2bu + (ac + b - 4d)u + c - abc + a d = 0.
Falls a, b, c, d reell ist, gibt es ein reelles u mit 4u ≤ a2.
3 2
Die Lösung der Gleichung 3. Grades mit u + a u + a u + a mit
2 1 0
2 2 2
a =-2b, a = (ac + b - 4d) und a = c - abc + a d siehe hier.
2 1 0
Dann errechnen sich die Koeffizienten, p,q und s,t folgendermaßen.
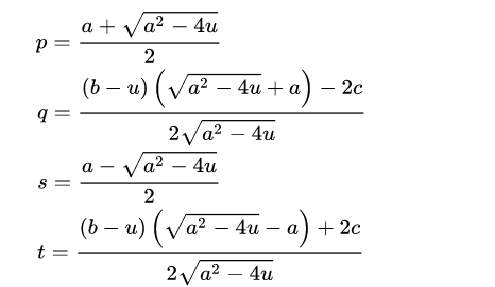
(Sonderfall a2-4u=0 d.h. p=a/2 siehe hier ...)
Rechenschema
Passende Koeffizienten a, b, c, d hier änderna=6 b=18 c=30 d=25 a2=-2*b a1=a*c+b^2-4*d a0=c^2+a^2*d-a*b*c v=12*a1^3-3*a1^2*a2^2-54*a1*a2*a0+81*a0^2+12*a0*a2^3 w=(36*a1*a2-108*a0-8*a2^3+12*sqrt(v))^(1/3) u=(w^2-12*a1+4*a2^2-2*a2*w)/(6*w) z=sqrt(a^2-4*u) p=(a+z)/2 q=((b-u)*(z+a)-2*c)/(2*z) s=(a-z)/2 t=((b-u)*(z-a)+2*c)/(2*z) probe_a=s+p probe_b=t+p*s+q probe_c=p*t+q*s probe_d=q*t x1=-p/2+sqrt((p/2)^2-q) x2=-p/2-sqrt((p/2)^2-q) x3=-s/2+sqrt((s/2)^2-t) x4=-s/2-sqrt((s/2)^2-t) probe1=x1^4+a*x1^3+b*x1^2+c*x1+d probe2=x2^4+a*x2^3+b*x2^2+c*x2+d probe3=x3^4+a*x3^3+b*x3^2+c*x3+d probe4=x4^4+a*x4^3+b*x4^2+c*x4+d
In Maple
a:=6; b:=18; c:=30; d:=25; a2:=-2*b; a1:=a*c+b^2-4*d; a0:=c^2+a^2*d-a*b*c; v:=12*a1^3-3*a1^2*a2^2-54*a1*a2*a0+81*a0^2+12*a0*a2^3; w:=(36*a1*a2-108*a0-8*a2^3+12*sqrt(v))^(1/3); u:=simplify((w^2-12*a1+4*a2^2-2*a2*w)/(6*w)); z:=sqrt(a^2-4*u); p:=simplify((a+z)/2); q:=simplify(((b-u)*(z+a)-2*c)/(2*z)); s:=simplify((a-z)/2); t:=simplify(((b-u)*(z-a)+2*c)/(2*z)); probe_a:=s+p; probe_b:=t+p*s+q; probe_c:=p*t+q*s; probe_d:=q*t; x1:=simplify(-p/2+sqrt((p/2)^2-q)); x2:=simplify(-p/2-sqrt((p/2)^2-q)); x3:=simplify(-s/2+sqrt((s/2)^2-t)); x4:=simplify(-s/2-sqrt((s/2)^2-t)); probe1:=x1^4+a*x1^3+b*x1^2+c*x1+d; probe2:=x2^4+a*x2^3+b*x2^2+c*x2+d; probe3:=x3^4+a*x3^3+b*x3^2+c*x3+d; probe4:=x4^4+a*x4^3+b*x4^2+c*x4+d;Bemerkung: Manche Rechenprogramm können u nicht weiter vereinfachen. Dann ergibt der Rest der Rechnung sehr komplizierte Ausdrücke.
Beispiel: x4+3x3+7x2+7x+6=0
a=3 b=7 c=7 d=6 p=1 q=2 s=2 t=3
—
-1±i√7
x =——————
1,2 2
—
x =-1±i√2
3,4
Beispiel: x4+6x3+18x2+30x+25=0
a=6 b=18 c=30 d=25 p=3+3i q=5*i s=3-3i t=-5*i x1=-2-i x2=-1-2i x3=-1+2i x4=-2+i
Beispiel: x4+x3+x2+x+1=0
ergibt die Einheitswurzeln von x5-1=0 cos(n·72°)+isin(n·72°) für n=1,2,3,4.
a=1
b=1
c=1
d=1
p=1/2+(sqrt(1/2*sqrt(5)+5/4))*i
q=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i
s=1/2+(sqrt(1/2*sqrt(5)+5/4))*i
t=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i
—————
1 1 — 1 / —
x =-—+—√5 + —i√10+2√5 = cis(72°)
3 4 4 4
—————
1 1 — 1 / —
x =-—-—√5 + —i√10-2√5 = cis(2·72°)
4 4 4 4
—————
1 1 — 1 / —
x =-—-—√5 - —i√10-2√5 = cis(3·72°);
1 4 4 4
—————
1 1 — 1 / —
x =-—+—√5 - —i√10+2√5 =cis(4·72°)
2 4 4 4
x1=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i=cis(3*72°)
x2=(1/4*sqrt(5)-1/4)+(sqrt(1/8*sqrt(5)+5/8))*i=cis(4*72°)
x3=(1/4*sqrt(5)-1/4)+(sqrt(1/8*sqrt(5)+5/8))*i=cis(72°)
x4=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i=cis(2*72°)
Beispiel: x4-x3+x2-x+1=0
a=-1 b=1 c=-1 d=1 p=(-1/2)+(sqrt(1/2*sqrt(5)+5/4))*i q=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i s=(-1/2)+(sqrt(1/2*sqrt(5)+5/4))*i t=(-1/4-1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i x1=(1/4+1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i=cis(36°+4*72°) x2=(-1/4*sqrt(5)+1/4)+(sqrt(1/8*sqrt(5)+5/8))*i=cis(36°+3*72°) x3=(-1/4*sqrt(5)+1/4)+(sqrt(1/8*sqrt(5)+5/8))*i=cis(36°+72°) x4=(1/4+1/4*sqrt(5))+(sqrt(5/8-1/8*sqrt(5)))*i=cis(36°)
Beispiel: x4+2x3-14x2+2x+1=0
a=2 b=-14 c=2 d=1 p=1-1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17))+1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17)) =-0,158941651 q=(-1/2-1/2*sqrt(17)+1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17)))*(1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2-1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17)))=-0,07362017 s=1-1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17))+1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17)) =2,158941651 t=(1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2+1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17)))*(-1/2-1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17)))=-13,58323408 x1=-1/2-1/2*sqrt(17)+1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17))=-0,203258342 x2==1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2-1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17))=0,362199993 x3=1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2+1/2*sqrt(14-2*sqrt(17)) =2,760905633 x4=-1/2-1/2*sqrt(17)-1/2*sqrt(14+2*sqrt(17))=-4,919847284
Beispiel: x4+x3-4x2+x+1=0
a2=8 a1=13 a0=6 v=0 w=5+5isqrt(3) u=-1 p=1/2+1/2*sqrt(5) q=-1/2*sqrt(5)-3/2 s=-1/2*sqrt(5)+1/2 t=-3/2+1/2*sqrt(5) x1=-3/2-1/2*sqrt(5) x2=1 x3=1 x4=-3/2+1/2*sqrt(5)
Beispiel: x4+x3-3x2+x-4=0
a2=6 a1=26 a0=0 v=137904 w=6+2*sqrt(51) u=0 p=0 q=1 s=1 t=-4 x1=i x2=-i x3=-1/2-1/2sqrt(17) x4=-1/2+1/2sqrt(17)
Beispiel: x4+x2+2x+1=0
w=(-152+48*i*sqrt(51))^(1/3); u=1/2+1/2*sqrt(17) z=i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17)) p=1/2*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17)) q=-1/4*sqrt(17)+1/4+1/4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17)) s=-1/2*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17)) t=-1/4*sqrt(17)+1/4-1/4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17)) x1=-1/4*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17))+1/4*sqrt(-6+2*sqrt(17)-4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17))) ≈-0,624810534-0,30024259i x2=-1/4*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17))-1/4*sqrt(-6+2*sqrt(17)-4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17))) ≈0,624810534-1,30024259i x3=1/4*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17))+1/4*sqrt(-6+2*sqrt(17)+4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17))) ≈0,624810534+1,30024259i x4=1/4*i*sqrt(2+2*sqrt(17))-1/4*sqrt(-6+2*sqrt(17)+4*i*sqrt(-2+2*sqrt(17))) ≈-0,624810534+0,30024259i
Beispiel: x4-12x3+1222-388x+1241=0
a=-12 b=122 c=-388 d=1241 a2=-244 a1=14576 a0=-238784 v=-400919887872 w=(13967360+4386816*I*sqrt(3))^(1/3)≈248+41,5692193816530552i u=164 z=16*sqrt(2)*i p=(-6)+8*sqrt(2)i q=(-21)-20*sqrt(2)i s=(-6)-8*sqrt(2)i t=(-21)+20*sqrt(2)i x1=(3-sqrt(2))+(4*sqrt(2)-2)*i≈1,585786438-3,656854249i x2=(sqrt(2)+3)+(2+4*sqrt(2))*i≈4,414213562-7,656854249i x3=(sqrt(2)+3)+(2+4*sqrt(2))*i≈4,414213562+7,656854249i x4=(3-sqrt(2))+(4*sqrt(2)-2)*i≈1,585786438+3,656854249i
Herleitung Rechenschema
x4+ax3+bx2+cx+d=(x2+px+q)(x2+sx+t) (Gleichung *)
4 3 2 2 2
x + ax +bx +cx +d = (x +px+q)·(x +sx +t)
1. Schritt: Bestimme eine Lösung u der Gleichung 3. Grades
3 2
u +a bu + a u + a = 0 für
2 1 0
2 2 2
a =-2b, a = ac+b -4d und a = c +a d - abc
2 1 0
Eine Lösung u für u3+a2u2+a1x+a0=0 ergibt sich folgendermaßen
v=12*a1^3-3*a1^2*a2^2-54*a1*a2*a0+81*a0^2+12*a0*a2^3 w=(36*a1*a2-108*a0-8*a2^3+12*sqrt(v))^(1/3) u=(w^2-12*a1+4*a2^2-2*a2*w)/(6*w)
Mit diesem Wert u erechnet sich p, q, r, s von (Gleichung *) folgendermßen:
z=sqrt(a^2-4*u) p=(a+z)/2 q=((b-u)(z+a)-2c)/(2*z) s=(a-z)/2 t=((b-u)(z-a)+2c)/(2*z)